Starting a startup in India requires proper legal registration and compliance to ensure smooth operations and access to government benefits. Whether you are an aspiring entrepreneur or a small business owner, registering your startup is a crucial first step. This guide explains the process of registering a startup in India step by step in 2025.
Understand the Startup Ecosystem in India
Before starting the registration process, it is essential to understand the startup ecosystem in India. The government offers several benefits for registered startups, such as tax exemptions, funding opportunities, incubation support, and easier compliance norms. Being aware of eligibility criteria, applicable government schemes, and legal structures will help you make informed decisions.
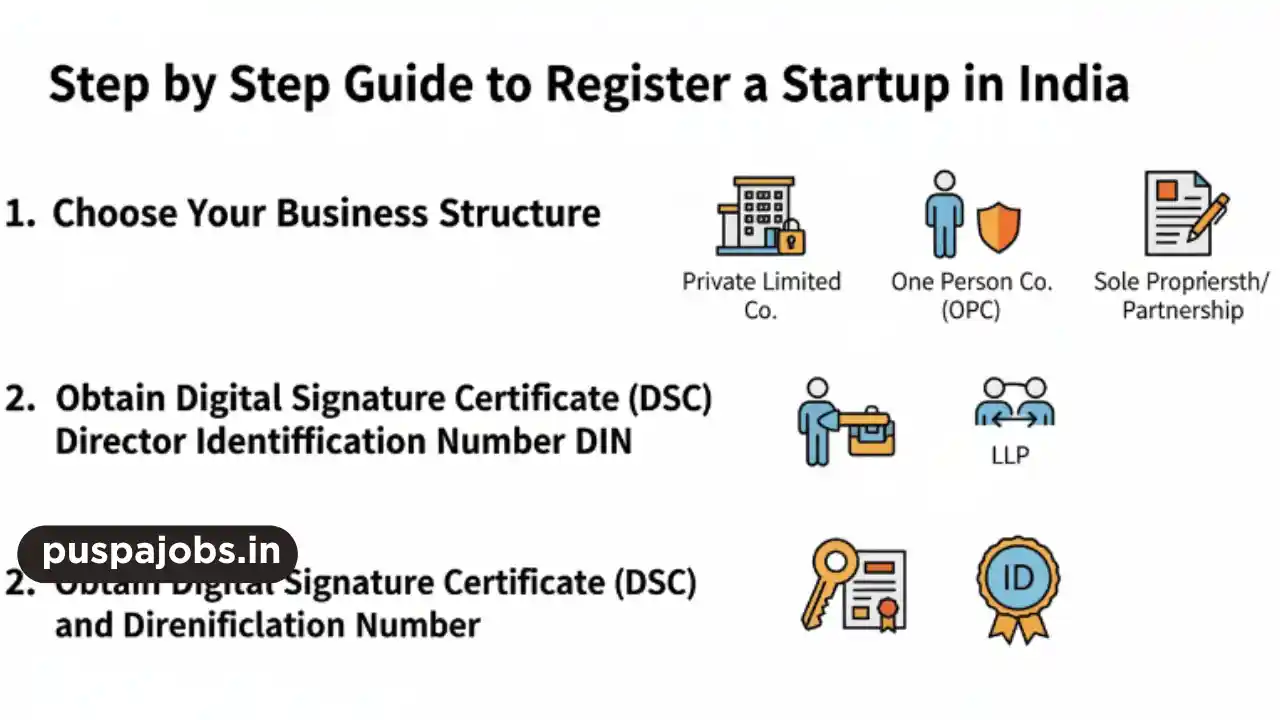
Choose the Type of Business Structure
Selecting the right business structure is critical for legal compliance and tax purposes. Common business structures in India include:
- Private Limited Company (Pvt Ltd): Suitable for startups seeking investment and scalability.
- Limited Liability Partnership (LLP): Combines partnership flexibility with limited liability.
- Sole Proprietorship: Ideal for small businesses with single ownership and minimal compliance.
- Partnership Firm: Traditional partnership suitable for small teams with shared responsibility.
The choice of structure affects your registration process, taxation, and funding options.
Obtain Digital Signature Certificate (DSC) and Director Identification Number (DIN)
For registering a Private Limited Company or LLP, you need a Digital Signature Certificate (DSC) for signing electronic documents. Additionally, obtaining a Director Identification Number (DIN) is mandatory for all directors of a company. These documents are essential for filing incorporation forms online.
Apply for Company Name Approval
Choosing a unique and meaningful company name is an important step. The name should comply with the Ministry of Corporate Affairs (MCA) guidelines. You can apply for name approval through the MCA portal. Once approved, this name will be used in all registration documents and official communication.
File Incorporation Forms with the MCA
After obtaining DSC, DIN, and name approval, the next step is to file incorporation forms with the Ministry of Corporate Affairs. The required forms include:
- SPICe+ (Simplified Proforma for Incorporating Company Electronically)
- AGILE-PRO (for GST registration, Employee State Insurance, and Employees Provident Fund registration)
Filing these forms online completes the legal registration process and grants your startup a Corporate Identity Number (CIN).
Apply for PAN and TAN
Once your startup is incorporated, you need to apply for a Permanent Account Number (PAN) and Tax Deduction and Collection Account Number (TAN). These are mandatory for taxation and conducting financial transactions in India.
Register for GST (if applicable)
If your startup’s annual turnover exceeds the threshold limit or if you are involved in interstate supply of goods and services, you must register for Goods and Services Tax (GST). GST registration allows you to collect tax from customers and claim input tax credit, ensuring legal compliance in business operations.
Obtain Other Licenses and Approvals
Depending on the type of business, you may need additional licenses such as:
- FSSAI license for food businesses
- Trade license from the local municipal authority
- Import Export Code (IEC) for trading startups
These licenses ensure that your startup operates legally and avoids penalties.
Register with Startup India (Optional but Beneficial)
The Startup India program offers numerous benefits, including tax exemptions, funding opportunities, and incubation support. Registering with Startup India requires submitting details about your business, founders, and incorporation documents. Once approved, your startup can access government schemes and support programs.
Conclusion
Registering a startup in India is a structured process that ensures legal compliance, access to government benefits, and credibility in the business ecosystem. By following this step-by-step guide, aspiring entrepreneurs can establish their startups efficiently, focus on growth, and leverage government incentives. Proper planning and adherence to legal formalities are key to a successful startup journey.