Organic farming is a growing sector in India, driven by increasing consumer demand for healthy, chemical-free food. For small farmers, organic farming offers an opportunity to earn higher profits while promoting sustainable agriculture. This guide provides a step-by-step business plan for small farmers to start organic farming in India in 2025.
Understand the Market and Demand
Before starting, research the local and regional demand for organic products. Organic fruits, vegetables, grains, dairy, and spices are increasingly sought after by urban consumers, health-conscious families, and retail stores. Identifying target customers helps in selecting crops, planning production, and marketing effectively.
Choose Suitable Crops
Select crops that are suitable for organic farming in your region. Popular options include:
- Vegetables: Tomatoes, spinach, carrots, bell peppers
- Fruits: Mangoes, bananas, guava, papaya
- Grains: Millets, rice, wheat
- Spices and herbs: Turmeric, coriander, mint, basil
Choosing high-demand crops ensures better profitability and marketability.
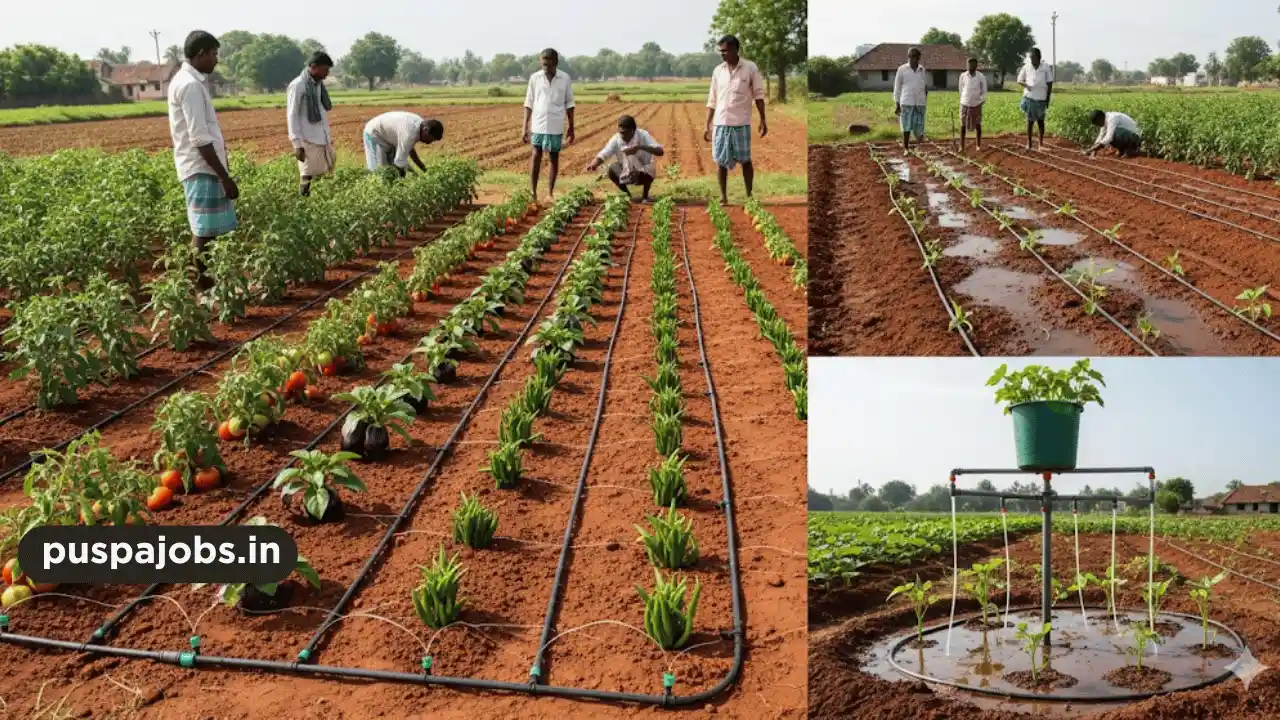
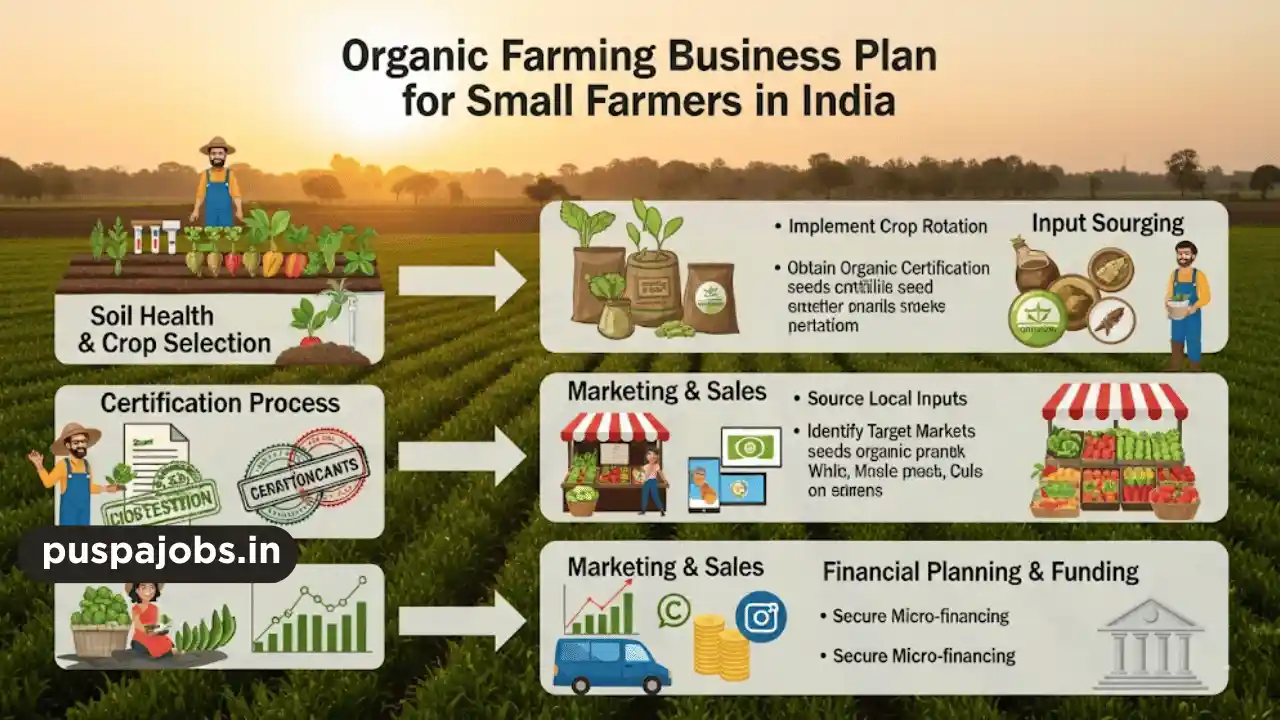
Prepare the Farm
Converting land for organic farming requires proper planning:
- Soil Testing: Determine soil fertility and nutrient requirements.
- Organic Fertilizers: Use compost, cow dung, and green manure instead of chemical fertilizers.
- Water Management: Install efficient irrigation systems like drip or sprinkler irrigation.
- Crop Rotation: Plan crop rotation to maintain soil health and prevent pest infestation.
A well-prepared farm ensures healthy crops and sustainable yields.
Obtain Organic Certification
Organic certification enhances credibility and allows farmers to sell at premium prices. Agencies like APEDA, India Organic, and IFOAM provide certification services. Complying with organic standards ensures that products meet consumer expectations and regulatory requirements.
Marketing and Sales
Effective marketing is key to profitability:
- Sell directly to local markets, retail stores, and organic food outlets.
- Use online platforms like Amazon, BigBasket, and local e-commerce apps.
- Partner with organic cooperatives and farmer groups to expand reach.
- Highlight the health benefits and chemical-free nature of products to attract consumers.
Branding and storytelling help differentiate organic produce from conventional options.
Investment and Cost Management
Starting organic farming requires moderate investment in seeds, fertilizers, irrigation, and certification. Estimated investment for a small farm may range from ₹1,00,000 to ₹5,00,000 depending on land size and crop selection. Managing costs efficiently and leveraging government subsidies like Paramparagat Krishi Vikas Yojana (PKVY) can reduce financial burden.
Risk Management
Organic farming faces challenges such as pest attacks, erratic weather, and market fluctuations. Mitigate risks by:
- Using organic pest control methods
- Investing in crop insurance
- Diversifying crops to reduce dependency on a single product
- Keeping emergency funds for unforeseen situations
Proper risk management ensures long-term sustainability and profitability.
Scaling and Expansion
Once established, small farmers can scale operations by:
- Expanding the farm or acquiring leased land
- Adding value-added products like organic jams, pickles, or juices
- Partnering with restaurants, supermarkets, and organic subscription boxes
- Implementing technology for soil monitoring and crop management
Scaling improves revenue, market presence, and long-term viability.
Conclusion
Organic farming is a profitable and sustainable business for small farmers in India. By choosing suitable crops, following organic practices, obtaining certification, and marketing effectively, farmers can achieve higher returns and build a strong reputation in the market. With careful planning, dedication, and efficient cost management, small-scale organic farming can become a successful venture in 2025 and beyond.