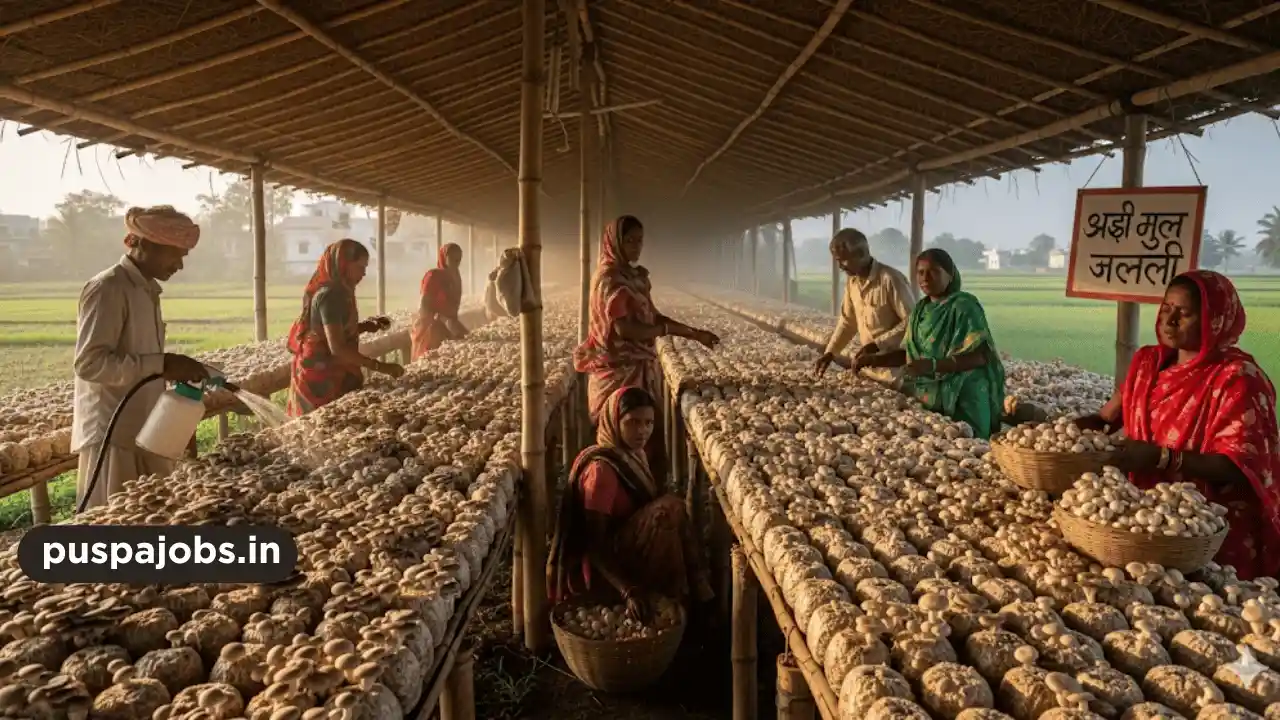
Mushroom farming has emerged as a profitable and sustainable agricultural business in India. With increasing demand for nutritious, high-protein foods, mushrooms offer a lucrative opportunity for small and medium-scale farmers. Starting a mushroom farming business requires minimal land, low investment, and can yield high returns if managed properly.
Understanding the Market
Before starting, it is crucial to understand the demand for mushrooms in your region. Common varieties like Button, Oyster, and Shiitake mushrooms are highly sought after in urban markets, restaurants, hotels, and supermarkets. Identifying target customers and distribution channels will help you plan production and marketing strategies effectively.
Choosing the Right Variety
The choice of mushroom variety determines both yield and marketability. Button mushrooms are most popular for commercial production, while Oyster and Shiitake mushrooms are considered premium varieties. Beginners are advised to start with Button mushrooms due to their easier cultivation process and quick growth cycle.
Setting Up the Farm
Mushroom cultivation can be done indoors or in controlled environments. Essential requirements include:
- Grow Room: A well-ventilated, humid, and temperature-controlled room.
- Substrate Preparation: Using materials like straw, sawdust, or compost enriched with nutrients.
- Spawning: Using quality mushroom spawn from certified suppliers.
- Irrigation and Humidity Control: Regular watering and maintaining 80–90% humidity.
Proper farm setup ensures consistent growth and high-quality yield.
Investment and Cost
Mushroom farming requires moderate investment, including costs for substrates, spawn, infrastructure, and labor. For a small-scale farm, initial investment can range between ₹50,000 to ₹2,00,000 depending on the scale. Efficient cost management and reinvesting profits help scale operations gradually.
Cultivation and Harvesting
The cultivation cycle depends on the mushroom variety. Button mushrooms typically take 30–40 days from spawning to harvesting, while Oyster mushrooms grow in 15–20 days. Maintaining optimal temperature, humidity, and hygiene is critical to prevent contamination and ensure healthy production.
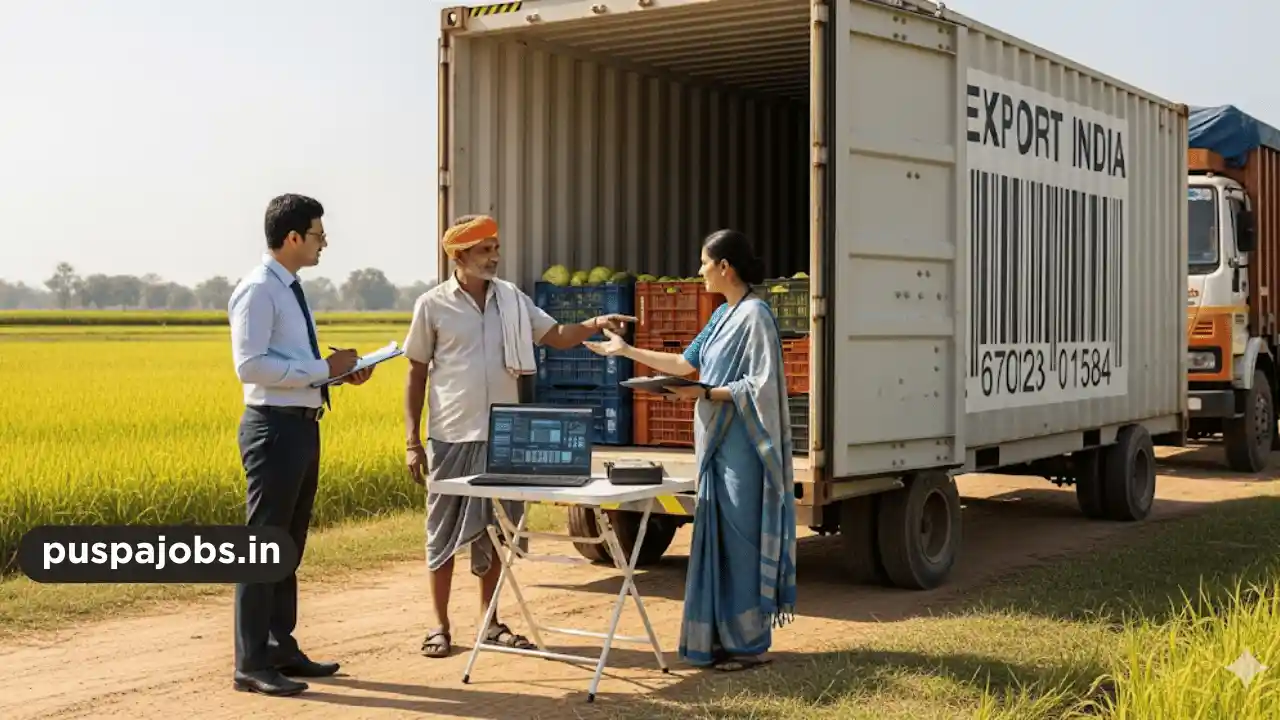
Marketing and Sales
Mushroom farmers can sell their produce directly to local markets, retail stores, hotels, restaurants, or through online marketplaces. Value-added products such as dried mushrooms, mushroom powders, and packaged fresh mushrooms can increase profit margins. Building relationships with buyers and maintaining consistent quality ensures repeat business.
Challenges and Risk Management
Mushroom farming faces challenges like contamination, fluctuating market prices, and environmental factors. Risk mitigation strategies include:
- Proper hygiene and sterilization practices
- Using high-quality spawn and substrates
- Diversifying mushroom varieties
- Monitoring market trends and consumer demand
Effective management minimizes losses and ensures sustainable profits.
Scaling the Business
Once established, mushroom farms can expand by increasing grow room capacity, adding new mushroom varieties, or introducing value-added products. Collaborating with local cooperatives, retail chains, and online food delivery platforms can further boost revenue and market presence.
Conclusion
Mushroom farming in India is a profitable and scalable venture that requires minimal land and investment. By selecting the right variety, maintaining optimal growing conditions, and implementing effective marketing strategies, entrepreneurs can build a successful mushroom farming business. With proper planning, dedication, and risk management, mushroom farming can become a sustainable source of income in 2025 and beyond.