Goods and Services Tax (GST) has simplified the taxation system in India, but for small businesses, filing GST correctly is crucial to avoid penalties and ensure compliance. Understanding the process, deadlines, and documentation helps entrepreneurs manage taxes efficiently and focus on growing their business.
Understanding GST
GST is a comprehensive indirect tax applied to the supply of goods and services in India. Small businesses with an annual turnover above the threshold limit are required to register for GST. Filing GST ensures legal compliance, eligibility for input tax credit, and smooth business operations. Common types of GST include CGST (Central GST), SGST (State GST), and IGST (Integrated GST for inter-state transactions).
Determine Eligibility and GST Registration
Small businesses must check if their annual turnover exceeds the GST threshold (₹20 lakh for most states, ₹10 lakh for special category states). Once eligible, businesses need to register on the GST portal. The registration process requires PAN, Aadhaar, business details, bank account information, and proof of business premises. A GSTIN (GST Identification Number) is issued upon successful registration.
Maintain Proper Records
Accurate record-keeping is essential for GST filing. Businesses should maintain invoices, purchase bills, sales registers, and input tax credit details. Proper documentation simplifies filing, reduces errors, and ensures compliance with GST regulations. Digital accounting software can help streamline record management for small businesses.
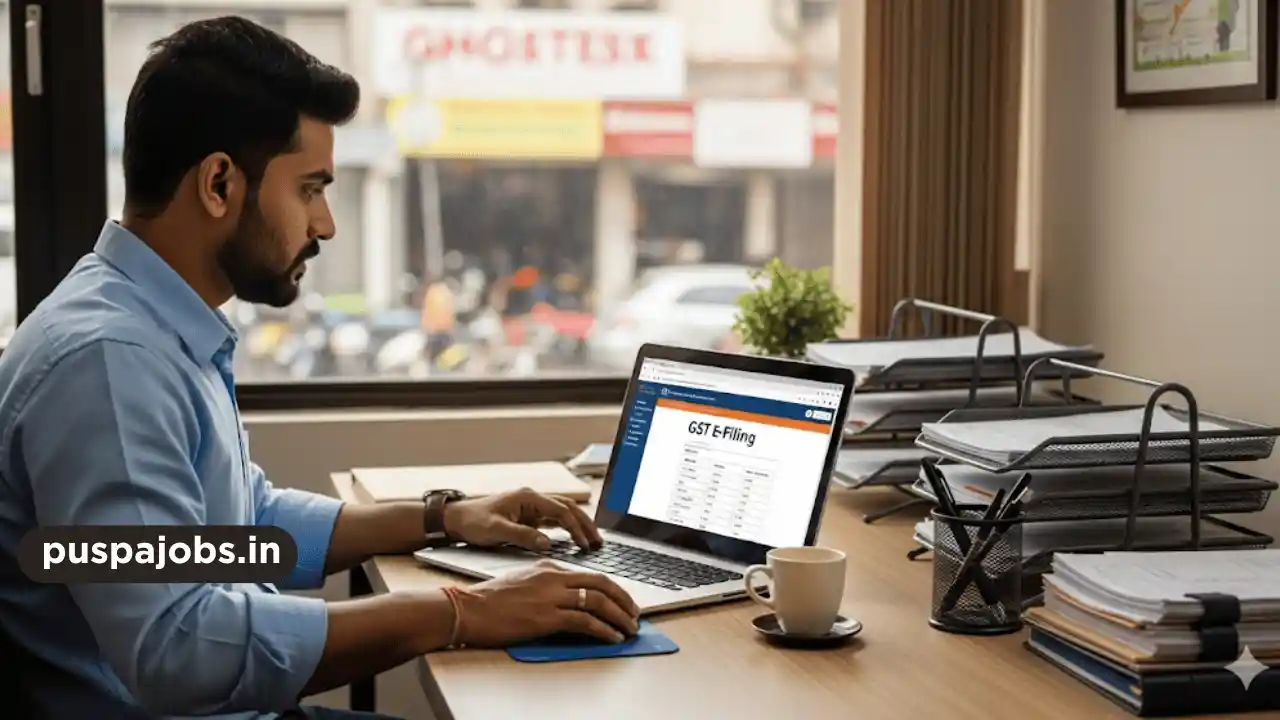
Filing GST Returns
GST returns are filed monthly or quarterly depending on turnover and type of registration. Common return forms include:
- GSTR-1: Outward supplies (sales)
- GSTR-3B: Summary of inward and outward supplies, tax liability, and payment
- GSTR-9: Annual return
Small businesses with turnover below ₹5 crore can opt for quarterly filing under Sahaj (for B2C) or Sugam (for B2B) schemes to reduce compliance burden.
Calculate Tax Liability
Calculate the total GST liability by considering outward supplies, inward supplies, and eligible input tax credits. Subtract the input tax credit from total tax payable to determine the net GST liability. Accurate calculation ensures timely payment and prevents penalties.
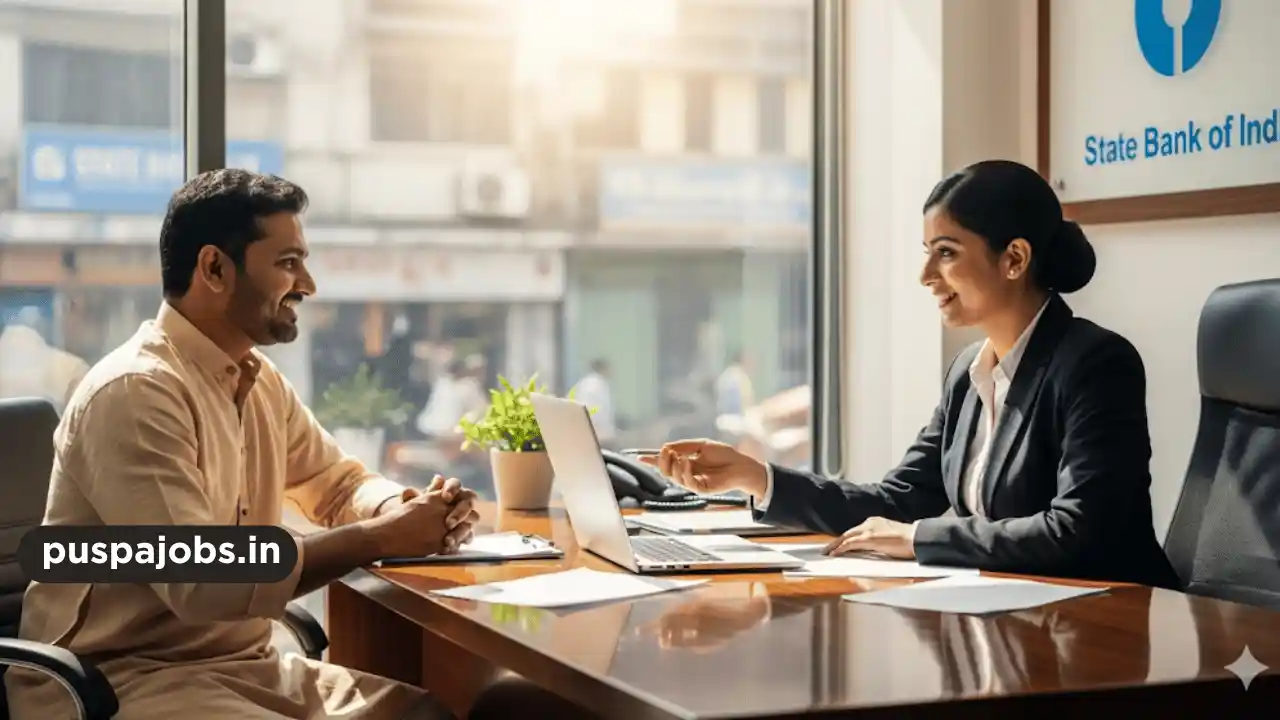
Make GST Payment
GST payment can be made online via the GST portal using net banking, debit/credit cards, or NEFT/RTGS. Timely payment before the due date avoids interest and penalties. Businesses should retain payment receipts as proof for future reference.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
To ensure smooth GST filing, small businesses should avoid:
- Delayed registration or filing
- Incorrect invoice details
- Ignoring input tax credit eligibility
- Late payment of tax
Regular training or consulting with GST experts can help prevent errors and streamline compliance.
Conclusion
Filing GST correctly is essential for small businesses in India to maintain compliance, avoid penalties, and benefit from input tax credits. By understanding GST registration, maintaining accurate records, calculating tax liability, and filing returns on time, entrepreneurs can manage taxes efficiently. With careful planning and disciplined processes, GST filing can become a simple part of running a successful small business in 2025 and beyond.